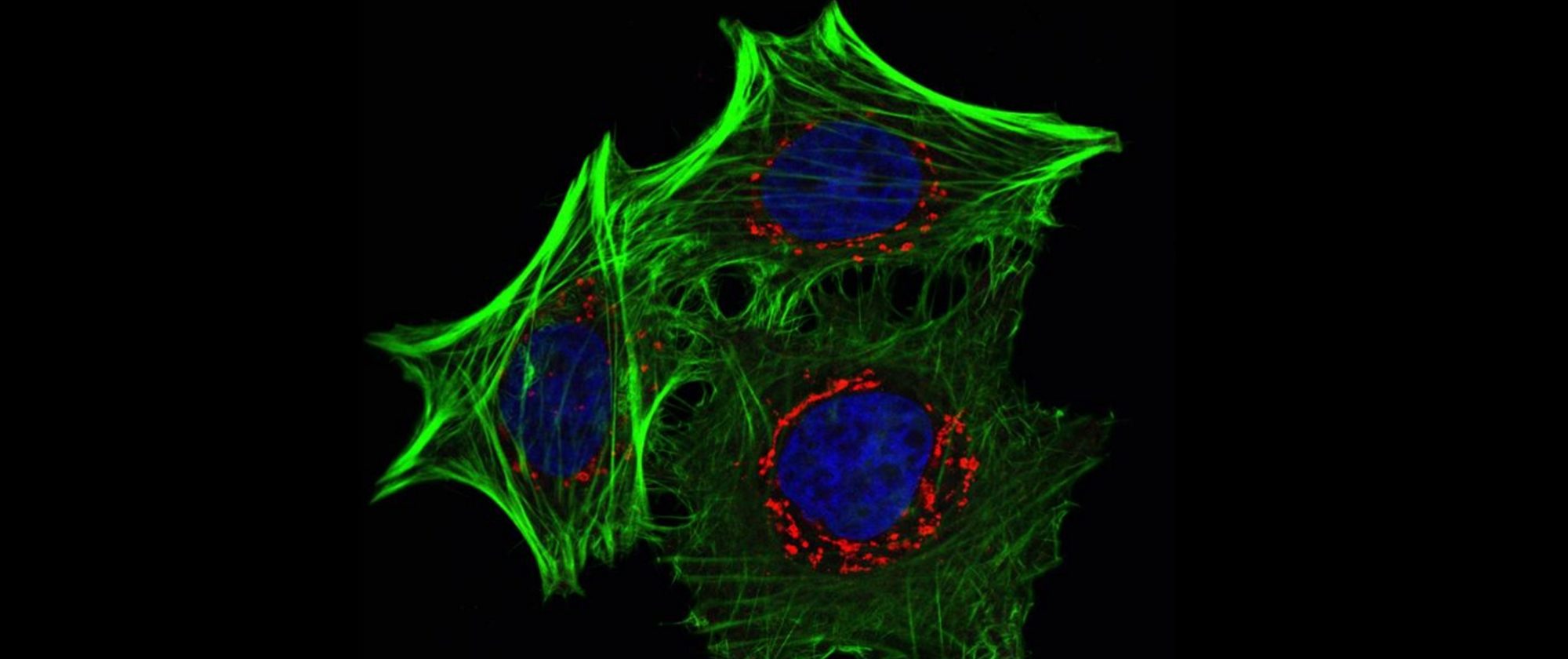
In this fluorescence microscopy image, taken by Julia Von Blume when she was at the Intracellular Compartmentation research group led by Vivek Malhotra at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), we can see some HeLa cells: the most common human cell type used in research. The cells were transfected with ADF/cofilin through a technique known as siRNA, which inhibits the targeted genes, in this case cofilin. The cells were then stained with phalloidin (seen in green), TGN46 (red) and DAPI (blue).
Phalloidin binds to actin filaments, one of the elements of the cell cytoskeleton. TGN46 is a marker for the Trans Golgi Network, which is basically a subdomain of the Golgi. The Golgi apparatus is the cell organelle responsible for packing newly formed proteins into membrane vesicles and sending them out to their final destination. The blue DAPI staining picks out the DNA in the cell nucleus.
In this experiment, the researchers were trying to understand the role of cofilin, a molecule that regulates actin-filament dynamics and seems to be involved in the selective sorting and export from the Golgi.
Would you like to see your photo here? Please send us pictures related to science or the PRBB to ellipse@prbb.org.