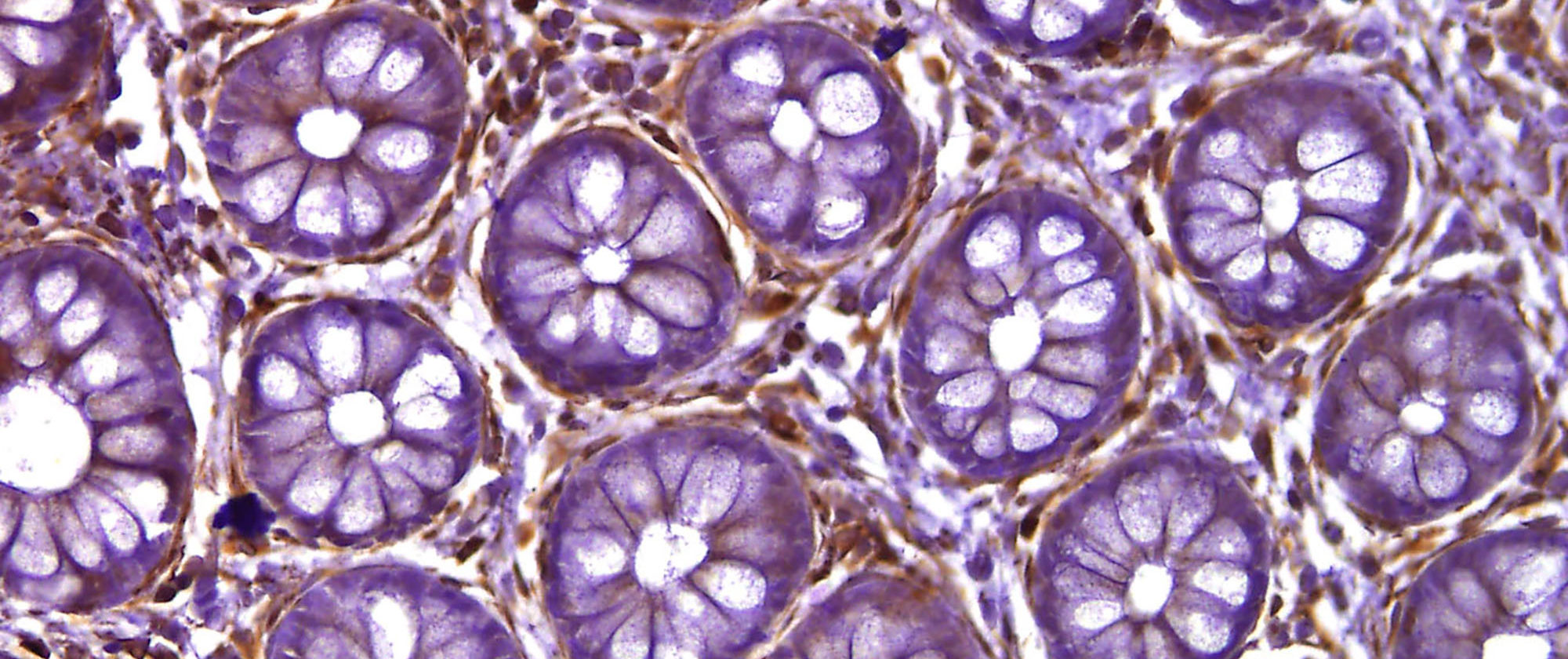
This image of a transversal cut of the colon, by Vanessa Fernández-Majada and Lluís Espinosa (Stem cells and cancer research group, Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM)), shows the intestinal crypts stained with haematoxylin and eosin. The aim was to detect the presence of the activated IKKa protein (in brown).
IKKa is a kinase that plays an essential role in the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway. This pathway is activated by multiple stimuli such as inflammatory cytokines, bacterial or viral products, DNA damages or other cellular stresses.
In healthy intestinal crypts such as those in the image, most of the cells are negative for this staining and the only brown cells are the lymphocytes that occupy the spaces in between the crypts. In colon tumour samples, on the other hand, there are high levels of activated IKKa.