Why is it that, when we are in love, we feel excited or we behave a bit obsessively towards the other person? The answer is a combination of the neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin and noradrenalin.
After all, we function thanks to a network of nervous cells, the neurons, which are connected amongst them. The neurons of the peripheral nervous system sense the external stimuli – a sound, an image – and they transmit them to the neurons at the central nervous system, in the spinal cord and the brain. Here all the information is integrated, and a response is sent through a return neuronal circuit.
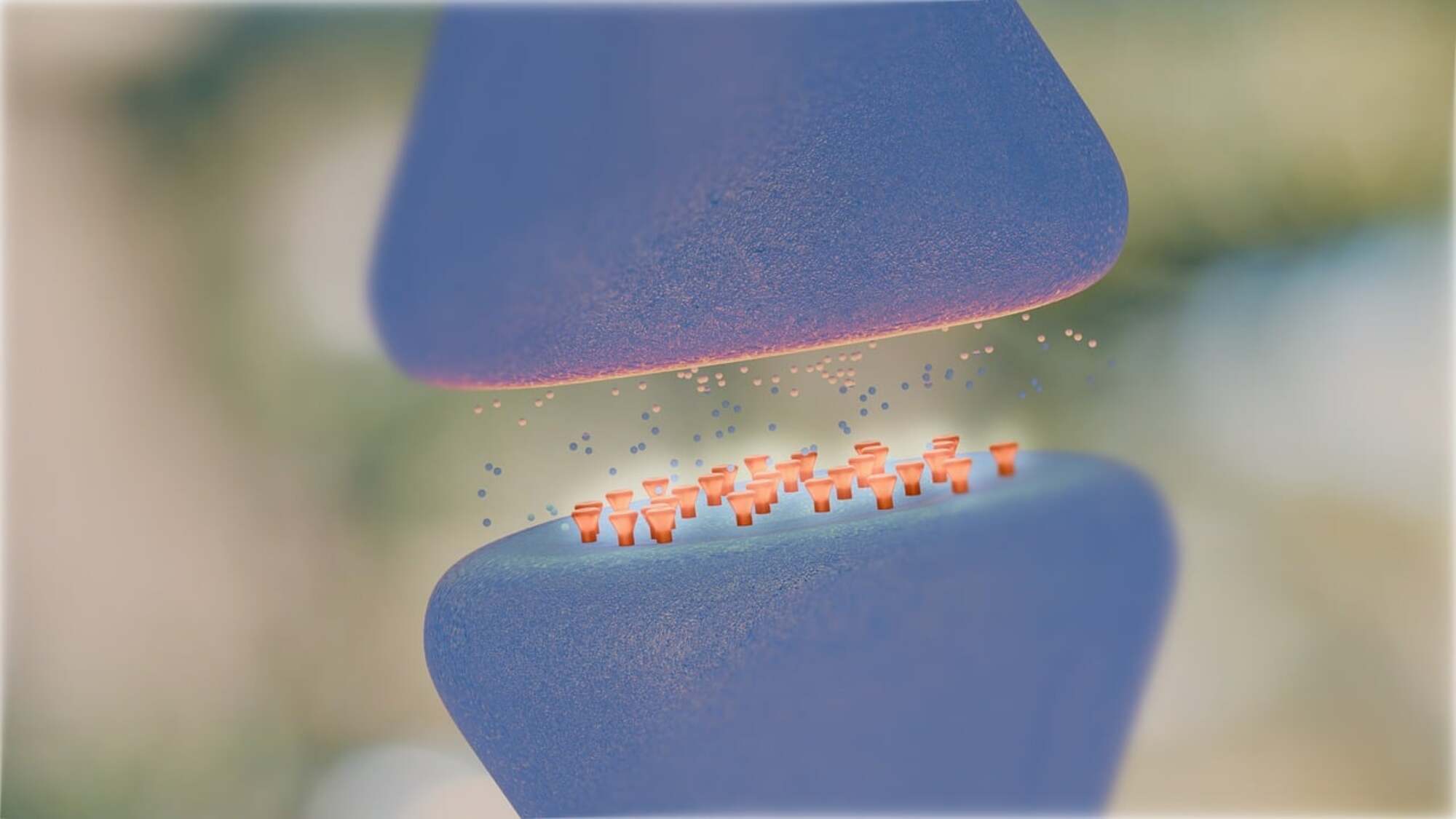
Neurotransmitters are the molecules that transmit the information from one neuron to another. There are different types of neurotransmitters. The classical ones are synthesized directly at the ends of the presynaptic neurons (those that emit the signal), where they accumulate in vesicles until they are liberated to the space between the two neurons, the synaptic space. From here they are picked up by the postsynaptic neuron, that which receives the signal.
- An example of classical neurotransmitter is dopamine, which is related with feelings of pleasure, motor function and emotions. One of the consequences of a lack of dopamine in the brain is Parkinson.
- Adrenaline is segregated in stress situations, and it causes the excitement of the peripheral organs, with an increase in the cardiac and breathing rhythm.
- In the central nervous system it is noradrenalin which is in charge of making the brain become alert, as well as controlling sleep patterns and increasing attention. The elimination of noradrenalin from the brain has been related to depression, while an excess is related to panic attacks.
- Serotonin is another classical neurotransmitter. Changes in its level are associated to mental disequilibria, such as schizophrenia or autism.
Other types of neurotransmitters, beyond the classical ones, include neuropeptides and some gases, such as nitric oxide.
But there are still many questions about neurotransmitters. Could the levels of neurotransmitters be modulated in chronic diseases without it leading to the loss of efficiency or the appearance of undesired effects? Does dopamine know that it has to be liberated only when we feel real love? Thousands of researchers all over the world, including some at the Barcelona Biomedical Research Park (PRBB), are trying to solve these mysteries by studying these diminutive molecules, the messengers of our thoughts, feelings and actions.