About 30% of patients with locally advanced rectal cancer relapse and metastasize, despite having undergone chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery. Now, a team of doctors and researchers from the Hospital del Mar and the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM) has shown that liquid biopsy – which makes it possible to detect DNA from tumor cells in the blood – serves to identify these patients.
“We have shown that we could find this circulating tumor DNA in patients with a localized tumor who had received chemotherapy or radiotherapy treatment. And we have validated the prognostic value of finding this DNA.”
“This study gives us the basis to launch a prospective clinical trial to analyze how to apply what we have discovered”
Clara Montagut (IMIM-Hospital del Mar)
A flexible tube for prostate cancer
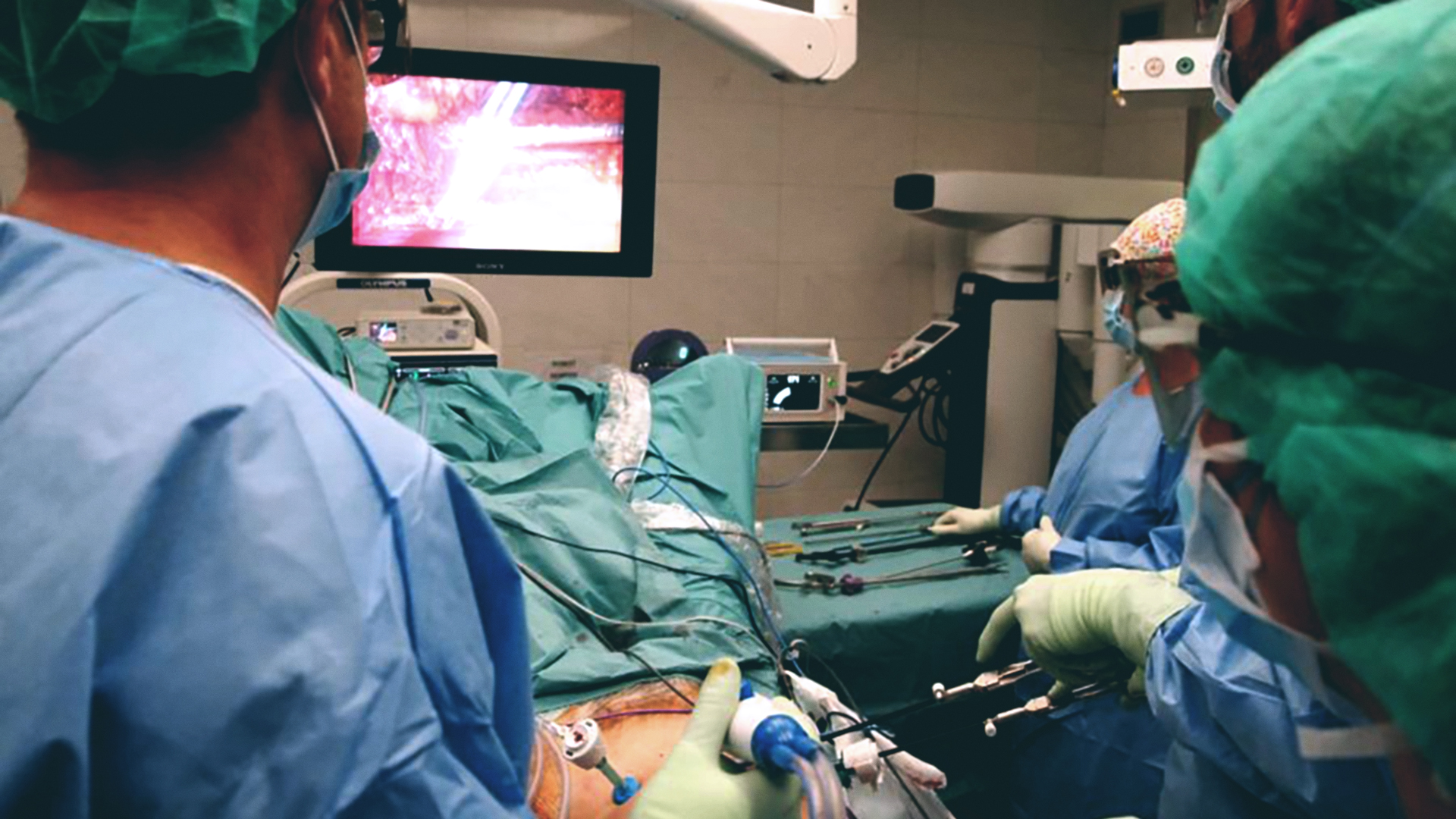
Another medical and scientific team of the IMIM-Hospital del Mar is pioneering a great advance in the treatment in this case of prostate cancer. The Hospital Urology Service is testing a miniaturized flexible probe that will allow a better detection of the marker used in patients to localize the sentinella ganglion, the first to which the tumor drains.
“It is a device with a cable that is introduced into the abdominal cavity of the patient and that can be manipulated with the usual instruments. It adapts better to the patient’s anatomy than the current rigid probes, increasing the sensitivity of detection”
Lluís Fumadó (IMIM-Hospital del Mar)
This probe, called SENSEI® and developed by the UK company Lightpoint Medical, will then be tested at five other hospitals in Germany, France, the UK, the Netherlands and Belgium.
Vidal J, Casadevall D, Bellosillo B, Pericay C, Garcia-Carbonero R, Losa F, Layos L, Alonso V, Capdevila J, Gallego J, Vera R, Salud A, Martin-Richard M, Nogué M, Cillán E, Maurel J, Faull I, Raymond V, Fernández-Martos C, Montagut C. Clinical Impact of Presurgery Circulating Tumor DNA after Total Neoadjuvant Treatment in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: A Biomarker Study from the GEMCAD 1402 Trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 16. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4769. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33727257.